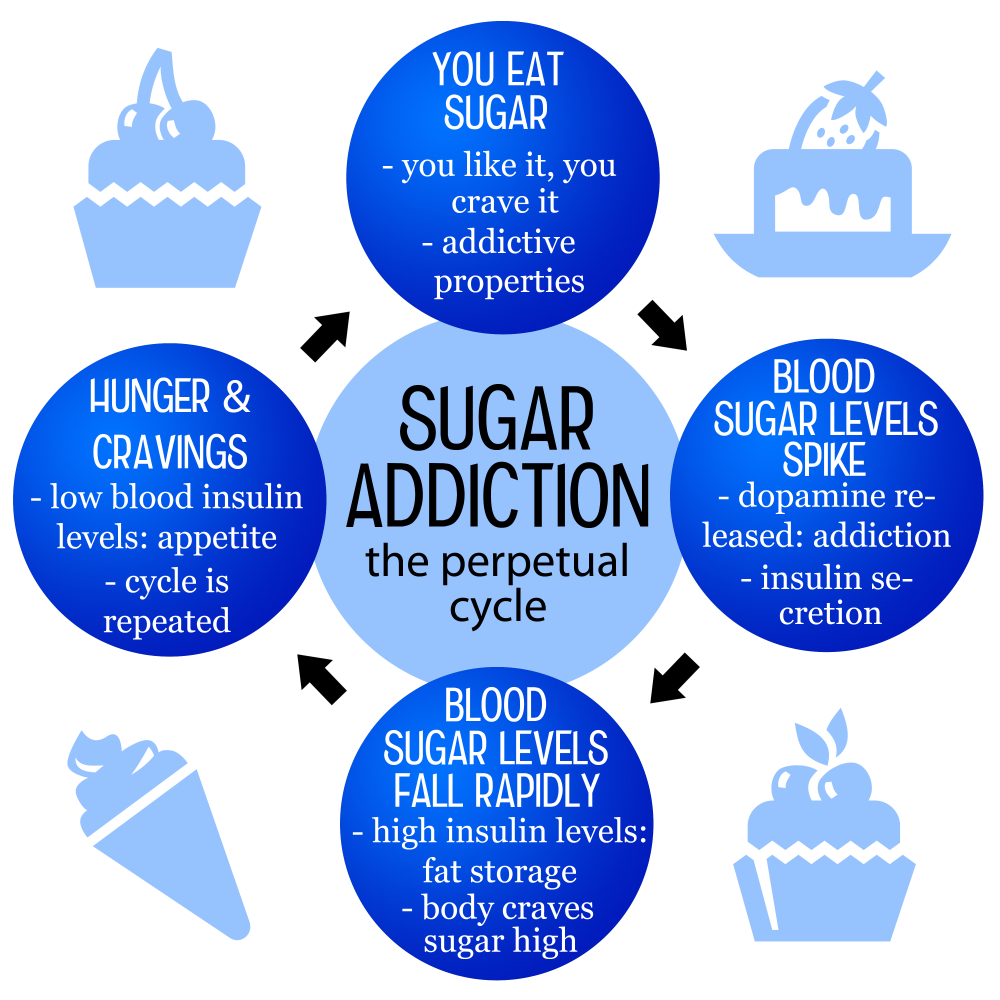
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked intense debate among nutritionists and researchers alike, as sugar seems to elicit cravings that mirror those triggered by substance addictions. While it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, the health effects of sugar cannot be ignored; they contribute to both physical and psychological responses, such as mood swings and withdrawal symptoms when removed abruptly from our diets. The prevalence of sugar in processed foods compounds the issue, as these items are engineered to be highly palatable, making them difficult to resist. Understanding sugar consumption within the context of addiction may shed light on better dietary choices and healthier relationships with food.
When exploring the question of sugar’s potential addictive nature, it’s essential to consider alternative expressions of this concept. Terms like “sugar cravings” and “sugar addiction” convey the strong desire many people experience for sweet foods, often leading to habitual habits. Furthermore, the negative health implications associated with excessive sugar intake in our diets emphasize the importance of moderation in sweeteners found within processed foods. This discourse reflects broader themes in nutrition, including the balance between necessary nutrients and those that can lead to compulsive behaviors. Delving into the science behind these cravings can provide insight into managing sugar’s role in our lives and making informed dietary decisions.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The debate around sugar addiction continues to grow as more research sheds light on our relationship with sweeteners. While many liken cravings for sugar to traditional addictions like alcohol or nicotine, scientific classification does not currently support this claim. Sugar does induce cravings and can influence eating behaviors significantly; however, it lacks the severe withdrawal symptoms associated with recognized addictive substances. Nutrition experts caution that while sugar can create compulsive eating patterns, it is vital to approach the subject with nuance. Furthermore, the distinction between physiological addiction and habitual craving is critical in understanding why we continuously seek out sugar-laden processed foods.
One of the primary reasons sugar is often viewed as addictive is its prevalence in the modern diet, particularly within processed foods. Items like sugary snacks and beverages often flood the market, designed to be hyper-palatable, making them hard to resist. This leads to habitual sugar consumption which can result in withdrawal-like symptoms when trying to cut back. However, unlike drugs that can be fully eliminated from one’s lifestyle, sugar is naturally present in many essential foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, underscoring the importance of moderation. Recognizing the balance between necessary sugar intake and overconsumption is key to managing cravings without labeling sugar as a dangerous substance.
The Health Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
Diving into the health effects of sugar, it’s evident that excessive consumption can lead to numerous chronic health issues. The American Heart Association recommends limiting sugar to a maximum of 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 for women. Unfortunately, the average person surpasses these recommendations, often consuming nearly 20 teaspoons daily through processed foods. This excessive intake is linked to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other significant health ailments, indicating that being mindful of sugar consumption is crucial for maintaining overall health.
Moreover, the effects of sugar are not only physical but psychological as well. Many individuals experience mood swings or increased anxiety as a result of fluctuating blood sugar levels from large intakes of sugary foods. These psychological impacts of sugar consumption can fuel cravings for more sugar, creating a vicious cycle that may be mistaken for addiction. It’s essential for individuals to assess their sugar consumption and be aware of how it affects their physical health and mental well-being, establishing healthier eating habits going forward.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Managing sugar cravings is crucial for those concerned about their health but feel overwhelmed by their desire for sweets. One effective strategy is to gradually decrease the intake of added sugars rather than attempting to quit cold turkey, which can lead to a backlash of cravings. By slowly reducing sugar consumption, individuals can retrain their palates to appreciate natural sweetness found in whole foods like fruits. This approach not only satisfies cravings but also encourages a more balanced diet overall, promoting healthier eating patterns.
Additionally, incorporating more fiber and protein into meals can help mitigate sugar cravings. These nutrients promote satiety and stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing the urge for quick sugary fixes. Emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods in your diet can also play a significant role in regulating sugar intake. By being mindful of food labels and seeking alternatives to processed food, individuals can effectively manage their cravings and reduce overall sugar consumption, paving the way toward healthier lifestyle choices.
The Impact of Processed Foods on Sugar Habits
Processed foods are often loaded with added sugars, which contributes to increased cravings and potentially harmful eating habits. These foods are engineered to elevate flavors, making them more desirable and easier to consume in larger quantities. The high availability of these tasty yet unhealthy options creates an environment where it’s challenging to resist sugary snacks, leading to habitual consumption and a cycle of dependency. Understanding how processed foods impact sugar habits can empower individuals to make healthier choices.
Moreover, the rise of processed foods in our diets is directly linked to a growing number of health issues, including obesity and metabolic syndrome. Many fail to realize that even seemingly harmless snacks can contain excessive amounts of sugar. Education on reading food labels and recognizing hidden sugars is vital. By favoring whole, minimally processed foods over their highly processed counterparts, individuals can significantly reduce their added sugar intake and improve their overall health outcomes.
The Role of Sugar in Our Diets
While sugar often receives a bad reputation, it does play a role in our diets that should not be overlooked. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy are integral to a balanced diet, offering essential nutrients alongside calories. Sugar also enhances flavor, making healthy foods more enjoyable. However, the key is moderation, as excessive added sugars serve no nutritional purpose and can lead to significant health risks. Recognizing the difference between naturally occurring and added sugars is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet.
Furthermore, embracing the natural sweetness in wholesome foods can aid in reducing cravings for processed sugary items. Instead of eliminating sugar entirely, individuals should focus on moderation and mindful consumption. This means enjoying treats when desired but being aware of overall intake to avoid crossing into unhealthy levels. A sustainable approach to sugar in the diet enables individuals to satisfy their sweet tooth while maintaining health and well-being.
Recognizing Withdrawal Symptoms Related to Sugar Consumption
When considering sugar cravings, it’s essential to identify symptoms associated with reduced sugar intake. Many might experience withdrawal-like effects, including headaches, irritability, fatigue, or even anxiety when cutting back on sugary foods and beverages. While these symptoms are less severe than those experienced with drugs or alcohol, they still highlight the real psychological and physiological response to sugar reduction. Understanding these symptoms can prepare individuals for the early stages of reducing sugar.
Those who plan to decrease their sugar intake should anticipate these withdrawal symptoms and prepare accordingly. Gradually phasing out sugar allows the body to adjust without harsh reactions. Staying hydrated, consuming balanced meals with adequate protein and fiber, and finding healthier sweet alternatives can help ease this transition. By understanding and managing potential withdrawal symptoms, individuals can reduce their sugar intake more effectively.
The Psychological Effects of Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings can have profound psychological effects, often linked to behavioral patterns developed over time. These cravings can trigger feelings of guilt, stress, and anxiety, especially in a culture that celebrates sweet treats. Compulsive eating driven by these cravings can lead to unhealthy cycles where individuals seek comfort in sugary foods. Recognizing this relationship between sugar and emotional health is crucial for those seeking to break free from unhealthy eating habits.
To combat these psychological effects, individuals must develop healthier coping mechanisms. Mindfulness practices can be beneficial, teaching individuals to recognize cravings without immediately succumbing to them. Additionally, finding substitutes that fulfill the desire for sweetness through comprehensive diets rich in fruits and whole grains can shift focus away from processed sugary foods. By addressing the emotional aspect of sugar cravings, one can work towards healthier habits that foster both physical and mental well-being.
Building a Balanced Diet with Respect to Sugar
Maintaining a balanced diet where sugar is concerned involves understanding the roles that different types of sugars play. Natural sugars in whole foods provide nutrition alongside energy, while added sugars in processed items can lead to health complications when overconsumed. Emphasizing whole foods rich in fibers and nutrients not only satisfies hunger but naturally reduces cravings for added sugars. Adapting dietary habits to prioritize such foods contributes positively to long-term health.
Incorporating a range of flavors and textures in meals can also help in achieving dietary balance. Swapping out high-sugar snacks for naturally sweet options like fruits or using spices to enhance flavor can redirect cravings in a healthy direction. Striving for balance rather than total elimination of sugar often leads to better dietary adherence and satisfaction. In this light, sugar can play a harmonious role in a well-rounded diet.
Educational Resources for Managing Sugar Intake
Educating oneself about sugar intake and its effects is a stepping stone to managing consumption effectively. Numerous resources and programs are available that assist individuals in understanding the nuances of sugar in their diets. Websites, books, and workshops provide guidance on reading food labels, recognizing hidden sugars, and making healthier food choices. By leveraging these educational tools, individuals can empower themselves to take control of their health.
Moreover, seeking professional advice from nutritionists or dietitians can provide personalized strategies for reducing sugar intake. These professionals can offer tailored meal plans and strategies for coping with cravings, making the journey toward healthier eating less daunting. By taking advantage of these resources, individuals can foster healthier relationships with sugar and establish sustainable dietary habits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or drugs?
Sugar exhibits some addictive qualities, increasing cravings and causing compulsive eating behaviors, but it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or drugs. While users may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when sugar is reduced, the severity and impact differ significantly.
Why do I experience sugar cravings?
Sugar cravings can arise due to frequent consumption of processed foods, which are high in added sugars. These foods are not only palatable but also addictive in that they trigger pleasure centers in the brain, leading to habitual sugar consumption and cravings.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to significant health effects, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Regular consumption of high amounts of sugar can destabilize blood sugar levels, prompting cravings and contributing to unhealthy eating habits.
How does processed foods consumption relate to sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain added sugars, which can create cycles of cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The addictive qualities of these foods can encourage individuals to consume them repeatedly, making it hard to break the habit.
What is a healthy amount of sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women daily. Staying within these limits can help mitigate potential health risks and reduce the likelihood of sugar-related cravings.
Can reducing sugar consumption lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, reducing sugar consumption can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety for some individuals. Gradually decreasing sugar intake rather than stopping cold turkey is generally more manageable.
Is sugar found in healthy foods?
Absolutely! Sugar occurs naturally in many healthy foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products. It’s important to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars found in many processed foods.
What role does sugar play in our diet?
Sugar plays a role in enhancing flavor and texture in our food, contributing to enjoyment in eating. While it’s important to limit added sugars, a moderate amount of naturally occurring sugars can be beneficial.
How can I manage sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings, focus on balanced meals with whole foods that contain protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Gradually reducing added sugar in your diet and reading food labels can also help regulate intake and minimize cravings.
Are there any long-term effects of sugar addiction?
Long-term sugar addiction can lead to serious health issues, including increased risk of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and heart disease. Awareness and moderation are key to preventing these outcomes.
| Key Points | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance based on clinical criteria, unlike alcohol and nicotine. | Sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, leading to withdrawal-like symptoms when stopped suddenly. | Ultra-processed foods contribute to high sugar cravings due to their palatability and accessibility. | While sugar has addictive qualities, moderation is key and it is necessary for a balanced diet. | The average American consumes almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding recommended limits. | Gradually reducing sugar intake is advised instead of completely eliminating it. | Sugar enhances flavor and can contribute positively to our diets if consumed in appropriate amounts. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate around sugar’s addictive nature highlights the complexity of cravings and consumption habits. Although sugar does not meet the strict criteria for addiction, it can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to those seen in addictive substances. The presence of sugar in many foods, compounded by its palatable nature, makes it easy to overconsume. Moderation is essential; while sugar enhances the taste of foods, excessive intake can lead to health consequences. Understanding and managing sugar consumption through awareness and gradual reduction is key to a balanced and healthy diet.