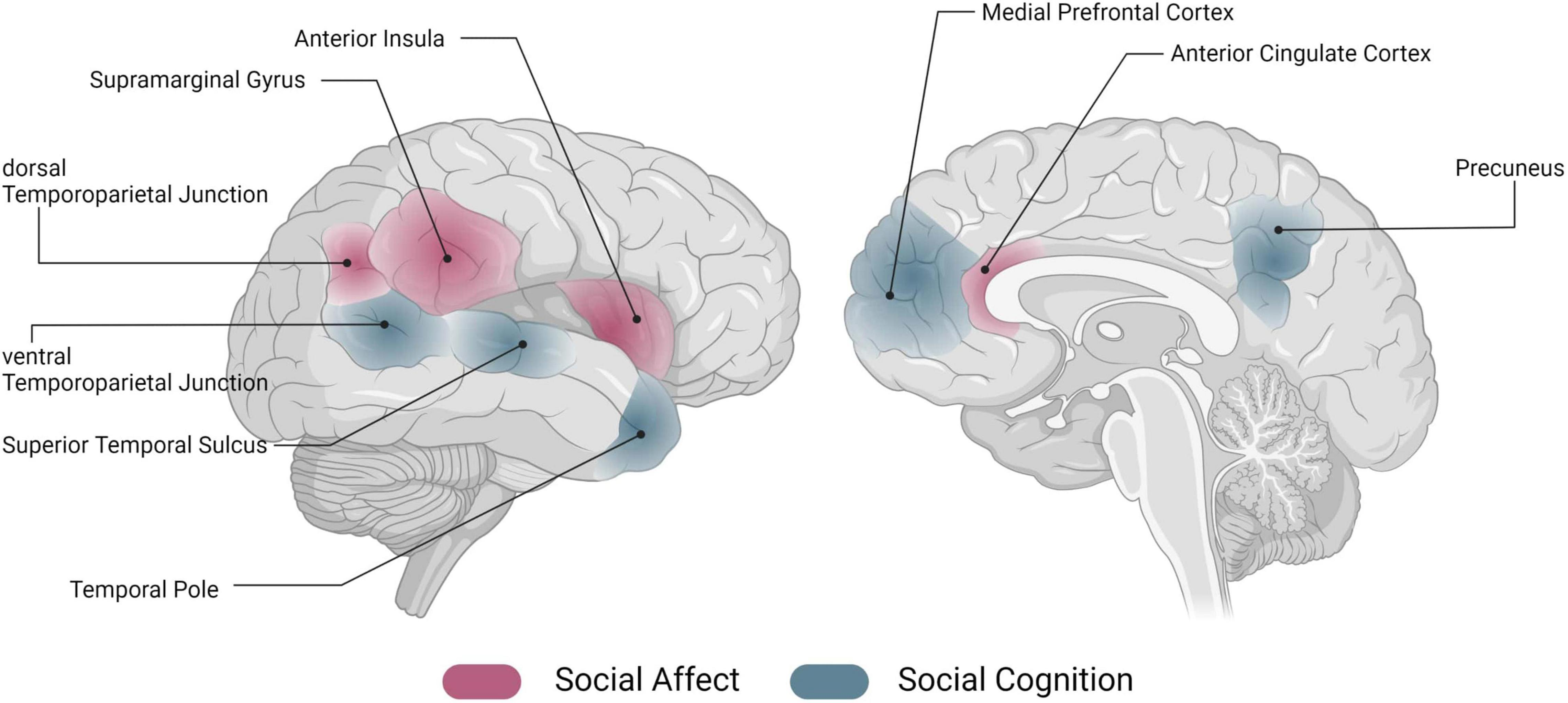
Social interaction neuroscience is a burgeoning field that investigates how our brains are wired to engage with others and the neural circuits that underlie our social behavior. As researchers delve deeper into the neuroscience of social behavior, they reveal the critical importance of social interaction for our mental and emotional well-being. Studies have shown that an absence of social connection can lead to profound effects on mental health, exacerbating issues such as loneliness and depression. By understanding the neural circuits and social needs that drive our interactions, scientists aim to address the public health concern surrounding social isolation. This research not only highlights human interconnectedness but also emphasizes the urgent need for social contact, akin to basic survival needs like food and water.
The study of the neural mechanisms behind social behavior brings to light the significance of human connections in our daily lives and how our brains facilitate these interactions. Often referred to as the biology of social behavior, this area of research uncovers the intricate pathways in our brain that compel us to seek companionship and form lasting relationships. With increasing evidence pointing towards the negative effects of social isolation on mental health, it is clear that fostering social bonds is essential. By exploring how our brain functions in response to social needs, experts can better understand the implications for emotional well-being and address the risks associated with loneliness in our increasingly digital age. Ultimately, unraveling the intricacies of how social engagement affects us biologically aids in reinforcing the importance of human connection in nurturing mental health.
Understanding Social Interaction Neuroscience
Social interaction neuroscience is an emerging field that investigates the underlying neural mechanisms driving our need for social connections. Research indicates that social behavior is not merely a byproduct of evolutionary processes but is deeply embedded in our neurological makeup. The interactions we engage in allow for the reinforcement of social bonds, which are crucial for our mental and emotional well-being. Neuroscientists are increasingly discovering that the circuits in our brains closely resemble those that regulate basic physiological needs, such as hunger and thirst, underscoring the critical role that social interaction plays in our day-to-day lives.
In recent studies, scientists have focused on the hypothalamus, the area of the brain responsible for maintaining homeostasis and regulating our social needs. By identifying neural circuits related to social interactions, researchers have been able to unveil how different factors, such as isolation or touch, can impact our mental health and social behavior. Understanding these circuits can foster new therapeutic approaches to conditions marked by social dysfunction, highlighting the significance of social bonds in facilitating overall mental health.
The Importance of Social Interaction for Mental Health
The importance of social interaction cannot be overstated when examining mental health and well-being. Social isolation has been linked to a myriad of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and even cognitive decline. Health professionals emphasize that human beings inherently crave social connections, which have a profound impact on emotional resilience and psychological stability. In essence, maintaining robust social networks is crucial for combating feelings of loneliness, enhancing one’s quality of life, and promoting positive mental health outcomes.
Moreover, understanding the neural basis of social interactions can shed light on how mental health issues disrupt this fundamental need. As research demonstrates, deprived social situations can affect not only our mood but also our physiological state, reminiscent of how hunger and thirst drive us to seek food or water. Thus, fostering environments that encourage social engagement may provide vital psychological support mechanisms, reducing instances of mental health complications linked to loneliness and isolation.
Neural Circuits and Their Role in Social Needs
Neural circuits play a critical role in mediating our social needs, much like they do for other fundamental requirements such as hunger and thirst. Recent studies involving animal models, specifically mice, have demonstrated how specific neurons in the hypothalamus become activated during periods of social deprivation. This research not only reveals the complexity of our social behavior but also emphasizes the biological imperative to connect with others, akin to our physiological drives.
Additionally, researchers have observed distinct phases during social interactions— “social seeking” during isolation and “social satiety” when reunited with peers. These findings indicate that the mind naturally seeks out social engagement, and prolonged isolation can alter an individual’s social preferences. Understanding these neural circuits not only emphasizes their importance in biological functions but also provides a framework for addressing social challenges in humans that stem from mental health disorders.
Effects of Social Isolation on Well-Being
The effects of social isolation are profound and troubling, aligning closely with the current public health concerns surrounding mental wellness. When individuals find themselves cut off from meaningful social interactions, the psychological repercussions can be debilitating. Research has indicated that long-term isolation can lead to an aversion to social contact, much like the adverse effects seen in individuals suffering from chronic stress or trauma. Understanding this phenomenon is essential for developing strategies to mitigate the harmful outcomes of prolonged isolation.
Furthermore, the current landscape of digital communication poses unique challenges, as many individuals opt for virtual connections over physical interactions. While technology can facilitate communication, it may not fulfill essential social needs for tactile engagement. As identified in the studies on social behavior, human interactions thrive on touch, which plays a fundamental role in establishing emotional bonds and promoting empathy. Recognizing these effects is crucial for developing interventions aimed at improving mental health and reducing the risks associated with loneliness.
Navigating Loneliness: Psychological and Neuroscientific Insights
Navigating loneliness is a complex endeavor, intertwining psychological and neuroscientific insights. As research indicates, loneliness is not merely about being alone; it relates to the perceived absence of quality social interactions that fulfill inherent needs. Neuroscientific studies have shown that loneliness triggers specific neurological responses that can lead to a decline in mental well-being. Understanding these dynamics will allow researchers and mental health professionals to tailor interventions that address both individual experiences and physiological responses to loneliness.
Additionally, employing psychological strategies such as improving social skills, fostering meaningful relationships, and even utilizing technology positively can help alleviate feelings of isolation. By recognizing the multifaceted nature of loneliness and the brain’s response to social deprivation, we can better equip individuals to foster satisfying social engagements, ultimately benefiting their overall mental health.
Touch: A Vital Component of Social Interaction
Touch is often overlooked in discussions about social interactions, yet recent research highlights its crucial role in human behavior. This fundamental sense can significantly influence our social preferences and emotional well-being. For instance, studies suggest that individuals who experience physical contact, such as hugging or handshaking, report higher levels of happiness and satisfaction in their social relationships. This underscores the notion that touch is a vital component in communication and social bonding.
Moreover, as societal norms shift towards more digital interactions, the absence of physical touch could exacerbate feelings of loneliness and mental health challenges. Understanding the importance of touch can help inform practices that encourage more meaningful physical interactions, potentially reducing the adverse effects associated with social isolation. This insight is particularly pertinent in our current digital age, where fostering tactile connections can greatly enhance the quality of social relationships.
The Biological Basis of Social Behavior
The biological basis of social behavior is an intriguing field that reveals how our brains are wired for connection. Through methods such as brain imaging, researchers can observe the intricate systems in our bodies that respond to social stimuli. This biological foundation plays a pivotal role in ensuring that social behavior is not just an option for survival but a necessity for thriving in a community.
Furthermore, understanding these biological underpinnings can illuminate how social behaviors are affected in situations of stress or trauma. When individuals encounter adversities that challenge their social capabilities, examining the biological responses can provide insight into therapeutic approaches that target specific neural pathways, potentially restoring a sense of normalcy and connection in their lives.
The Role of Neurons in Social Behavior
Neurons play an essential role in regulating social behavior, significantly influencing how individuals interact with one another. As research has illustrated, specific neural pathways in the brain activate during social engagement, directing attention toward social stimuli and fostering empathetic reactions. The interplay of neurotransmitters such as oxytocin, often dubbed the ‘love hormone,’ exemplifies how neurons facilitate social bonding, impacting behaviors and emotions.
Moreover, the adaptive responses of neurons to various social environments underline the complexity of social behavior. For instance, challenges such as bullying or social exclusion can alter neuronal responses, leading to heightened emotional distress. Understanding these neuronal activities and their respective influences can provide deeper insights into mental health treatment strategies that aim to enhance social functioning and reduce isolation.
Overcoming Social Isolation Through Community Engagement
Overcoming social isolation is paramount for improving mental health outcomes, and community engagement plays a vital role in this process. By fostering a sense of belonging and connection, community initiatives can challenge the loneliness epidemic plaguing many individuals. Engaging in local groups, volunteer activities, or social events creates opportunities for individuals to connect, build relationships, and gain support, ultimately enhancing their emotional and mental well-being.
Community engagement not only combats isolation but also strengthens social networks and promotes resilience among individuals. By participating in shared activities, individuals can experience the therapeutic power of social connection, which is essential for fostering mental health. Therefore, initiatives aimed at enhancing community involvement can significantly reduce the mental health burden associated with social isolation, encouraging individuals to rediscover the joys of companionship and collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neuroscience of social behavior and why is it important?
The neuroscience of social behavior explores how our brain functions during social interactions and why these interactions are critical for our well-being. It reveals that social connection is as vital as basic needs like food and shelter, helping us understand the neurological basis behind the importance of social interaction for mental health.
How do neural circuits relate to social needs?
Neural circuits governing social needs, as found in recent studies, function similarly to those regulating basic needs like hunger and thirst. Research has identified specific neurons in the hypothalamus that become active during periods of social isolation, emphasizing the biological basis of our need for social interaction.
What are the effects of social isolation on mental health?
Social isolation can lead to severe mental health issues, including increased feelings of loneliness and depression. Studies show that prolonged isolation alters our response to social interactions, suggesting a detrimental relationship between loneliness and mental health.
Why is understanding the effects of social isolation crucial in today’s society?
As social interactions increasingly occur online, understanding the effects of social isolation is essential. Research highlights that the lack of physical touch and face-to-face encounters can negatively impact our mental health, making it critical to find ways to maintain meaningful social connections.
How do sensory inputs contribute to social interaction needs?
Sensory inputs, particularly touch, significantly influence our social interaction needs. Research shows that even when visual or auditory contact is possible, the absence of tactile stimulation can trigger feelings of social deprivation, underscoring the need for physical interactions in fulfilling social needs.
What insights does the neuroscience of social behavior provide for improving mental health?
The neuroscience of social behavior offers insights into the biological foundations of our need for relationship-building. By understanding how social bonds affect our mental health, we can develop better strategies to foster social connections and combat the negative effects of social isolation.
How does the need for social interaction mirror basic physiological needs?
Recent research suggests that the need for social interaction may parallel basic physiological needs such as hunger and thirst. This perspective indicates that just like failing to meet these basic needs can lead to discomfort, inadequate social interaction can lead to feelings of loneliness and distress.
| Key Concept | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection | Considered a basic human need, comparable to food and shelter. |
| Research Findings | Study published in Nature reveals the neurological underpinnings of the need for social interaction. |
| Social Isolation | Highlighted by the U.S. Surgeon General as a significant public health concern. |
| Neural Basis | Study focuses on hypothalamus neurons occurring during social deprivation and reunion phases. |
| Touch and Social Needs | Touch is essential for fulfilling social needs, with implications for human behavior. |
| Implications for Mental Health | Understanding social interaction mechanisms helps address mental health issues related to social behavior. |
Summary
Social interaction neuroscience is crucial in understanding how our brain encodes the need for social connections, similar to how it processes basic physiological needs like hunger and thirst. Recent findings by researchers illustrate that social interactions are fundamental not just for emotional well-being, but also for our overall mental health. The insights gained from studying these neural circuits pave the way for addressing public health issues related to social isolation and mental illnesses, reinforcing the importance of face-to-face connections in an increasingly digital world.