Black and white infant mortality remains a pressing issue within American public health, revealing significant disparities despite overall improvements in life expectancy for both groups. Recent studies indicate that while mortality rates among adults have narrowed between Black and white Americans, the situation for infants has worsened dramatically, with Black infants now facing a mortality rate nearly double that of their white counterparts. This alarming trend highlights the stark healthcare disparities and racial health differences that persist in our society, demanding urgent attention from public health policy makers. The increase in Black infant mortality underscores the need for targeted public health initiatives aimed at addressing the systemic issues that contribute to these inequalities. As we strive to enhance healthcare access and quality, understanding the factors behind these trends is crucial to fostering a more equitable health landscape for all infants.
Infant mortality rates, especially across racial lines, reveal critical healthcare inequities that persist in America. The gap in mortality between African American and Caucasian infants serves as a barometer for the broader racial health differences that continue to plague our healthcare system. Despite advances in medical care and an overall increase in life expectancy, the persistent challenges faced by Black infants indicate a pressing need for reform in public health policy. As researchers explore the multifaceted causes contributing to these disparities, the spotlight remains on the paramount question of how to ensure equitable healthcare for all. Addressing these disparities not only promises to save lives but also fosters a more just society.
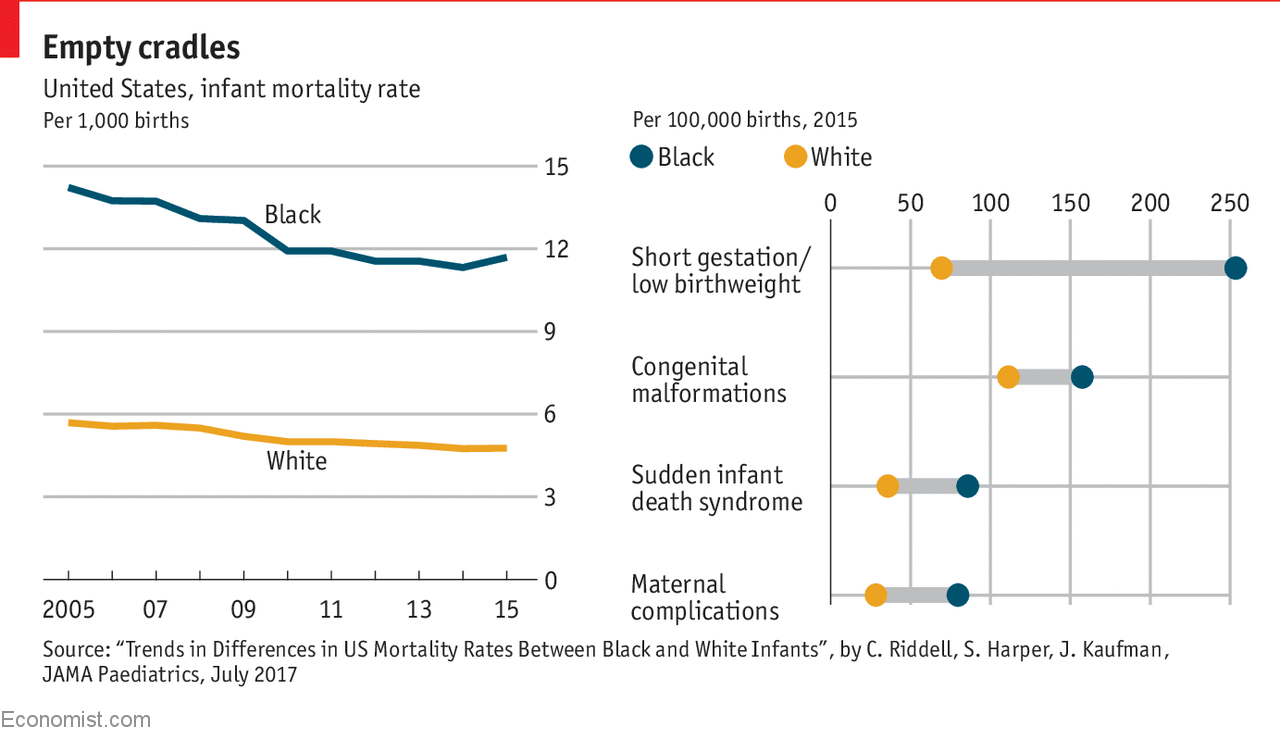
Infant Mortality Rates: A Stark Racial Divide
The recent analysis of infant mortality rates reveals a startling disparity between Black and white infants in America. Despite overall improvements in life expectancy for both races over the past seven decades, the neonatal health outcomes starkly highlight a failure in healthcare equity. In the 1950s, Black infants faced a mortality rate 92% higher than their white counterparts; this statistic has only worsened, with current figures showing a 115% increase in mortality rates. Such alarming numbers could point to systemic issues within healthcare that disproportionately affect Black mothers and infants, often rooted in social determinants of health that are overlooked in policy discussions.
This increase in infant mortality among Black infants brings to light essential questions about the efficacy of public health policies that have been implemented over the decades. As researchers have pointed out, while adult mortality rates show positive trends, this does not reflect the disparities felt within the infant population. It is crucial for public health frameworks to address these significant gaps and focus on targeted strategies that not only improve access to healthcare but also enhance the quality of care provided to minority communities. This focus is essential to ensure that both Black and white infants experience equitable health outcomes.
Healthcare Disparities and Racial Health Differences
The widening gap in infant mortality rates between Black and white infants highlights the alarming reality of healthcare disparities in America. It is critical to examine the broader context of racial health differences, especially in light of recent mortality statistics which show that, although life expectancy is increasing, Black Americans still face higher mortality rates overall. The systemic barriers to proper healthcare access and quality care remain significant challenges. In particular, studies indicate that Black infants encounter hurdles not only in accessing prenatal care but also in receiving adequate medical attention during childbirth, leading to preventable fatalities.
Moreover, these statistics beg the question of how public policy has evolved to address – or, in some cases, neglect – these disparities. Policymakers must prioritize initiatives that directly address the multidimensional aspects of healthcare inequality. This includes increasing funding for maternal and infant health programs that specifically target underprivileged communities. Understanding and addressing the intersection of socioeconomic status, education, and access to healthcare resources are vital steps toward mitigating the racial health differences that persist in America.
The Role of Public Health Policy in Addressing Disparities
Public health policy plays a crucial role in shaping the healthcare landscape, and it has a direct impact on outcomes for vulnerable populations. In light of the recent findings regarding Black and white infant mortality rates, there is a pressing need for health authorities to reevaluate their strategies and ensure that these policies equitably benefit all racial groups. Public health initiatives aimed at decreasing infant mortality must incorporate a comprehensive approach that includes community outreach, education, and access to culturally competent healthcare services.
Additionally, the recognition of healthcare as a social determinant of health is essential in crafting effective policies. Officials must acknowledge that healthcare disparities are not purely a matter of medical access but also interwoven with economic and social factors that dictate the overall health of communities. By implementing policies designed to address these root causes, the long-term goal of reducing the mortality rates of Black infants can become a reality. Collaborative efforts between health departments, community organizations, and policymakers can create a unified front against the inequalities faced by Black families in accessing healthcare.
Exploring Medical Conditions Leading to Higher Infant Mortality
Investigating the medical conditions that contribute to the high rates of infant mortality among Black infants reveals critical insights into the systemic issues plaguing the healthcare system. Inadequate prenatal care, gestational diabetes, hypertension, and other preventable medical conditions during pregnancy are frequently cited as leading causes of high infant mortality. These factors are compounded by disparities in healthcare access and quality, leading to the devastating outcome of increased infant deaths in Black populations. Understanding the specific medical conditions that disproportionately affect these families is imperative to informing better healthcare practices and policies.
Furthermore, the importance of targeted health interventions cannot be overstated. This includes not only improving access to prenatal and postnatal care but also providing education about potential health risks that could affect expectant Black mothers. Empowering these mothers through education and resources can lead directly to better health outcomes for their infants. Health care providers must be trained to recognize the unique challenges faced by these populations and approach care with cultural sensitivity and awareness of the socioeconomic factors influencing health.
Long-term Consequences of Racial Health Disparities
The long-standing racial health disparities reveal not only immediate health outcomes but also long-term consequences for entire communities. The impact of high infant mortality rates carries significant psychological and social repercussions. Families mourning the loss of a child face emotional trauma that can affect mental health and family dynamics for generations. These losses also have broader sociocultural implications, influencing community cohesion and the overall health narrative in Black communities. Addressing these issues head-on requires multifaceted approaches that resonate with the lived experiences of affected families.
Moreover, from a public health perspective, the ongoing prevalence of these disparities undermines collective progress toward improving health outcomes across the board. When a segment of the population faces preventable mortalities, it reflects failings in the system that ultimately impact the health and stability of society at large. To improve community health and life expectancy, it is vital for stakeholders to unite in their efforts to confront these inequities squarely, emphasizing investment in health resources, education, and policy reform that promotes equity.
Data-Driven Insights into Healthcare Inequity
Using data-driven insights is essential for a thorough understanding of healthcare inequity and its implications on infant mortality rates. The longitudinal study covering seven decades allows for a critical examination of how inequities have evolved over time and the effectiveness of various health policies. Such comprehensive analyses can highlight trends and reveal systemic issues that may otherwise remain hidden. For example, discrepancies in access to healthcare services can be better understood through meticulous data collection and analysis, ensuring that interventions are designed based on solid evidence rather than assumption.
Furthermore, gathering and analyzing data on infant mortality not only illustrates the disparities existing within the healthcare system but also provides a foundation for developing targeted public health campaigns. Implementing research-led strategies enables policymakers and health officials to tackle the crucial areas needing reform, ultimately striving for equality in health outcomes. The necessity for ongoing research is paramount to monitor changes and formulate responsive policies that address gaps in care for marginalized communities.
Engaging Communities in Health Discussions
To effectively combat the rising infant mortality rates among Black infants, community engagement must be at the forefront of health discussions. Community involvement is fundamental in understanding the unique challenges and cultural dynamics that affect health outcomes. By fostering dialogue between healthcare providers and community members, public health initiatives can be tailored more accurately to meet the needs of specific populations. Engaging communities allows for shared ownership of health issues and can empower individuals to advocate for necessary changes within the healthcare system.
Moreover, community-led approaches can catalyze essential health education and resource dissemination efforts that directly address the factors contributing to infant mortality. Support groups, informational sessions, and tailored health programs can significantly influence the perception and understanding of healthcare among expectant Black mothers. Ultimately, fostering community partnerships is essential in building trust and collaboration between healthcare providers and the communities they serve, leading to improved health outcomes for infants and families alike.
The Future of Public Health Interventions
Looking ahead, the future of public health interventions depends on the ability to integrate lessons learned from past disparities into actionable strategies. Addressing Black and white infant mortality must involve a comprehensive approach that encompasses healthcare access, quality of care, and systemic reform. Policymakers must prioritize allocating resources to programs that specifically target improving minority health outcomes, utilizing ongoing research to guide these efforts effectively. This highlights the necessity for a broad, unified commitment to health equity, ensuring that future generations of infants have an equal chance at a healthy start in life.
In conclusion, addressing the disparities in infant mortality rates involves a multifaceted approach that includes improving healthcare systems, engaging communities, and crafting informed public health policies. The insights gleaned from historical data serve as crucial indicators for where efforts should be concentrated to yield the most impactful results. The time to act is now; tackling these disparities isn’t just a healthcare issue but an urgent moral imperative for society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current infant mortality rates among Black and white infants in the U.S.?
As of the latest findings, Black infants die at a rate approximately twice that of white infants, indicating a significant healthcare disparity. The mortality rate for Black infants is reported to be 115 percent higher than that of white infants.
How do healthcare disparities affect Black and white infant mortality?
Healthcare disparities significantly impact Black and white infant mortality by contributing to unequal access and quality of care, which results in higher infant mortality rates among Black infants. Addressing these disparities is crucial for improving overall health outcomes.
What factors contribute to the differences in infant mortality rates between Black and white infants?
The differences in infant mortality rates between Black and white infants are largely attributed to medical conditions during pregnancy, access to healthcare, and the overall quality of care provided to mothers and infants.
Why has the disparity in infant mortality between Black and white infants worsened since the 1950s?
Despite improvements in overall healthcare and life expectancy, the disparity in infant mortality rates between Black and white infants has widened due to persistent systemic healthcare inequalities that have not been adequately addressed.
What role do public health policies play in addressing Black and white infant mortality disparities?
Public health policies are essential in addressing the racial health differences reflected in Black and white infant mortality rates. Policymakers must prioritize initiatives that reduce disparities, improve access to prenatal care, and enhance health education among communities.
How has life expectancy changed for Black and white Americans, and what does this mean for infant mortality?
Life expectancy for both Black and white Americans has improved over the past 70 years; however, this progress has not translated to equal improvements in infant mortality rates, particularly for Black infants, highlighting ongoing healthcare disparities.
What data sources were used to assess Black and white infant mortality trends?
The study analyzed data collected across the U.S. from 1950 to 2019, focusing on infant mortality rates as well as broader healthcare outcomes for both Black and white Americans.
What can be done to reduce Black and white infant mortality disparities in the future?
To reduce infant mortality disparities, there must be a concerted effort to address the underlying healthcare inequalities, enhance access to quality prenatal and postnatal care, and implement comprehensive public health policies targeting affected communities.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Americans are living longer than ever; overall mortality rates between Black and white Americans have narrowed since the 1950s, except for infant mortality. |
| Black infants are dying at twice the rate of white infants today, with the mortality gap worsening from 92% in the 1950s to 115% currently. |
| The leading cause of excess death among Black infants is linked to medical conditions during pregnancy, highlighting systemic healthcare inequalities. |
| Over the past 70 years, despite improved life expectancy, healthcare disparities between races persist, especially in infant mortality. |
| Public policy and health authorities need to prioritize addressing these disparities, as many lives could have been saved. |
Summary
Black and white infant mortality remains a significant issue, with disparities worsening over the past 70 years. While life expectancies have improved for both racial groups, the mortality rate for Black infants has drastically increased compared to their white counterparts, highlighting deep-rooted healthcare inequalities. Moving forward, it is crucial for policymakers and public health officials to address these alarming disparities and implement strategies that can save lives and promote equitable healthcare access.